The Role of the Ilizarov Technique in Bone Deformities
Bone deformities are significant orthopedic issues characterized by structural abnormalities of the bone, either congenital or acquired. These deformities lead to functional loss, pain, and cosmetic concerns, negatively impacting patients’ quality of life. Various treatment methods have been developed for bone deformities, among which the Ilizarov technique has revolutionized the correction of complex deformities. This article will discuss the scientific principles, treatment areas, and benefits of the Ilizarov method in detail.
History and Scientific Basis of the Ilizarov Technique
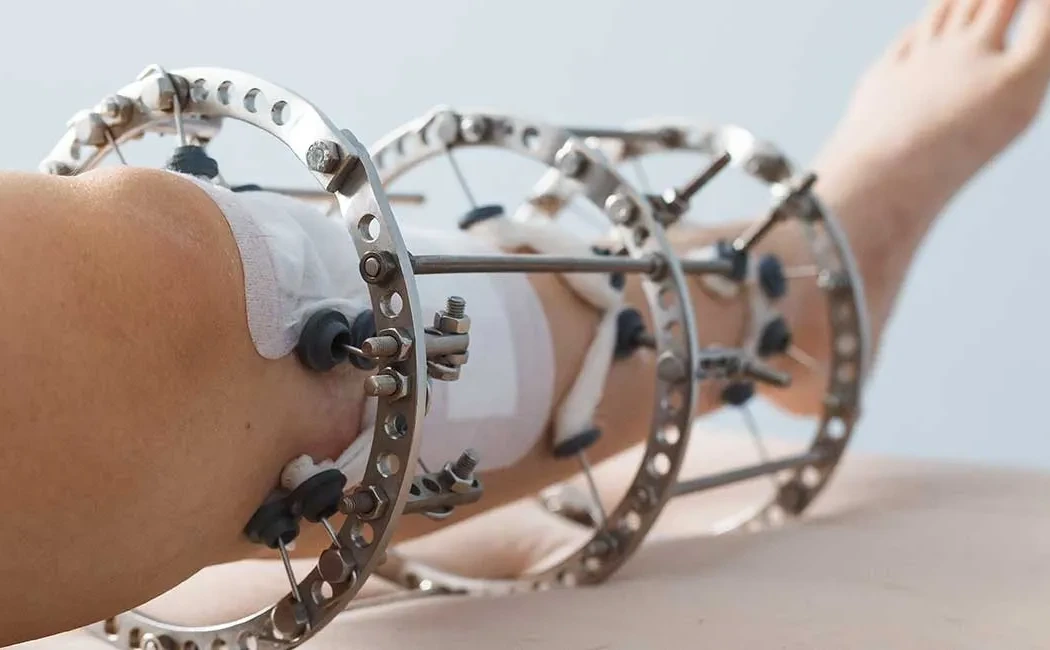
Developed in the 1950s by Russian orthopedic surgeon Gavriil Abramovich Ilizarov, this technique allows external stabilization of bones and controlled treatment. The Ilizarov apparatus consists of circular rings, rods connecting these rings, and wires passed through the bone. The fundamental principle is "distraction osteogenesis," a controlled process of bone stretching and tissue regeneration. After small bone cuts (osteotomies), the device gradually separates bone segments, inducing new bone and soft tissue formation in the created gap. This results in bone lengthening or deformity correction.
One of the most critical features of the Ilizarov technique is that not only bone but also soft tissues are stretched and reshaped simultaneously, enabling successful treatment even for severe deformities. This method is also widely preferred for nonunion fractures, infected fractures, and hard-to-heal wounds.
Applications of the Ilizarov Method in Bone Deformities
1. Limb Lengthening and Cosmetic Lengthening Surgery:
In surgeries aimed at increasing height, an osteotomy is performed at the fracture site, and the bone is slowly lengthened using the device over several weeks. This process promotes controlled growth of both bone and surrounding soft tissues. In cosmetic applications, planning the amount and duration of lengthening is vital.
2. Deformity Correction Surgery:
The Ilizarov device allows controlled correction of bone curvature or rotational deformities. Depending on the deformity type, the surgeon performs an osteotomy and adjusts the device to gradually bring the bone into the desired position.
3. Nonunion Treatment:
In cases where fracture healing is delayed or absent, bone biology can be revitalized by this method, along with providing mechanical stabilization to accelerate healing.
4. Bone and Soft Tissue Infections:
In infected areas such as open fractures or osteomyelitis, after surgical debridement, the Ilizarov device is used to stabilize the bone and maintain the area for treatment of infected tissues.
5. Reconstruction after Bone Tumors:
Segmental lengthening or bone transport can be performed with the Ilizarov technique to repair defects following tumor resection.
Advantages of the Ilizarov Technique
- It is a minimally invasive treatment that avoids large surgical incisions.
- It allows simultaneous adaptation of bone and soft tissue.
- Enables correction of long and multi-axial deformities simultaneously.
- Effective in treating nonunion and infected fractures.
- Patients can maintain partial mobility with the device, promoting early movement.
- Postoperative adjustments are manageable by the surgeon via the device during treatment.
Treatment Process and Patient Management
Treatment with the Ilizarov device usually lasts several months. After osteotomy, controlled lengthening and corrections continue over time. This phase requires cooperation and patience from both surgeon and patient. Regular follow-up and device care are essential to prevent infections. Physical therapy and rehabilitation support functional recovery.
With advances in computer-aided planning, Ilizarov surgeries have become more precise, reducing complication rates. Modern modifications also enhance device comfort.
Overall, the Ilizarov technique can be considered the gold standard for complex bone deformities. When properly planned by experienced surgeons, it achieves high success rates, minimizes complication risks, and provides patients with functional and aesthetic restoration.